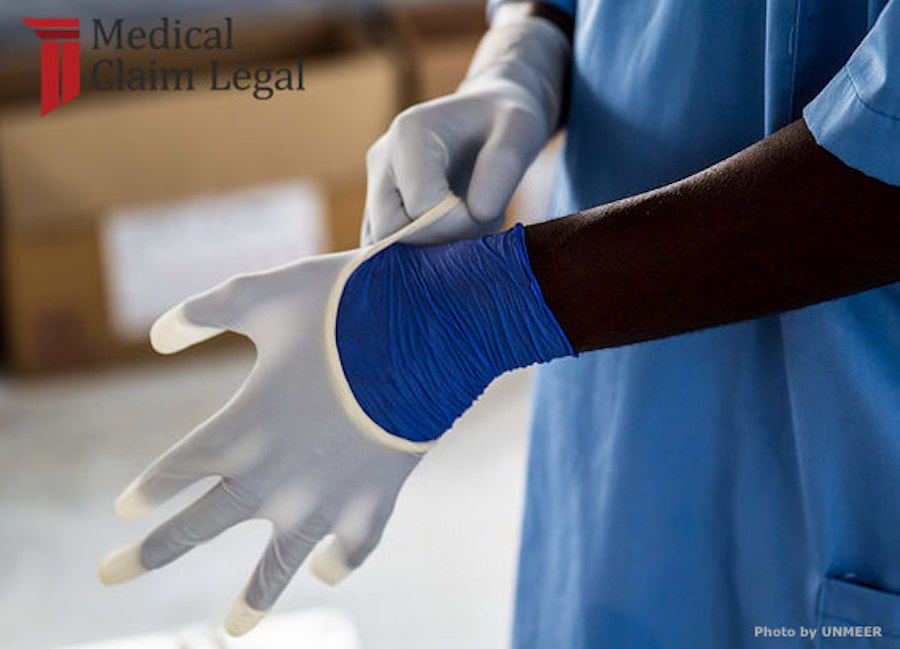
The use of most powdered medical gloves has been banned by the FDA.
For only the second time in history the FDA has banned a medical device. Powdered medical gloves seem to pose adverse risks.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has found that powdered medical gloves (powdered surgeon’s gloves, powdered patient examination gloves, and absorbable powder for lubricating a surgeon’s glove) “present an unreasonable and substantial risk of illness or injury.” This has led to a new rule banning these products from use, effective January 18, 2017.
One group has called the ban “18 years too late.” Nearly 20 years ago, in 1998, the advocacy group Public Citizen, filed the first of several citizen’s petition calling on FDA to ban powdered gloves.
After the ban was proposed by the FDA, Public Citizen responded saying that “when a medical product, drug or, in this case device, has unique serious risks but no unique benefit, it should be banned. The FDA’s statement that “we … only take this action when we feel it’s necessary to protect the public health” ignores overwhelming evidence going back almost two decades about the necessity to do so.”
Back in March of 2016, the FDA had prosed the powdered medical gloves citing evidence that they were a danger to patients, risks included airway and wound inflammation, post-surgical adhesions and allergic reactions.
Powdered gloves aim to make the removal of gloves easier for medical professionals. So, the FDA had to determine whether the ease of use outweighed the risks.
The rules not that powder is fine when used in the manufacturing process, but should not be a part of the finished product. The rule from the FDA “encourages manufacturers to ensure finished non-powdered gloves have as little powder as possible.”
If you believe that you or a loved one might have suffered from the medical use of powdered gloves, let the Medical Claim Legal Team help.